Effect of PCI devices on Automation Systems
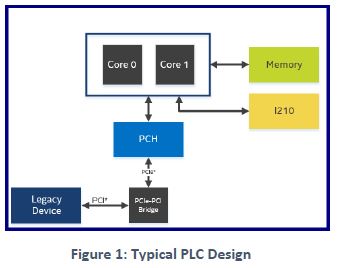
Figure 1 shows a typical industrial Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) design where one core is dedicated to Windows* supporting an application running a legacy device (such as a PCI device) and the other core is dedicated to a RTOS that supports a real time application running on Intel® Ethernet controller I210.
Industry 4.0 is changing systems architecture across all domains in industrial automation. Upcoming edge computing architectures use virtualization for scaling dedicated applications with deterministic key performance indicators (KPIs) on a heterogeneous operating systems. This enables an industrial control application to be configured to have dedicated cores assigned to different operating systems. For example, a motion controller can have a core dedicated to real time operating system (such as VxWorks*) to execute real-time workloads and another core assigned to a general purpose operating system (such as Windows*) to run other applications that are not time-sensitive.
Legacy device application run on Windows* and often frequently initiate bulk and high-speed data transfers from the CPU to the device via the system network. Real-time application run on RTOS and also demand system network resources by generating continuous compute requests to CPU core (for example, real time application running on Intel® Ethernet Controller I210 generate interrupts to be executed via the interrupt service routine (ISR)).. As time progresses, transactions from legacy device congest the system network as PCI-express to PCI Bridge stalls the ongoing traffic because PCIe ordering rules don’t support such bulk high-frequency data transfers to a PCI device. This degrades the Quality of Service (QoS) and disturbs the time synchronization for real time application. In cloud computing, this phenomena is known as the “noisy neighbor” effect.
